What’s in Your Food: All You Need to Know About Food Preservatives on the Labels
Eating well is easy with fresh produce but it can be a challenge when shopping for packaged food that is loaded with artificial additives. Here's our comprehensive guide to eating healthy without harmful preservatives.

Eating well is easy with fresh produce but it can be a challenge when shopping for packaged food in the local super market. Let’s admit it, we’ve all gulped down that carton of juice and snacked on a packet of chips without taking the time to read the list of preservatives that go into them.
For the uninitiated, preservatives are a type of food additive that is put into packaged food to prolong its shelf life, enhance the taste or keep the colour and nutrients of the product intact.

Photo Source
While a majority of these additives have been deemed safe for consumption by food authorities (in limited amounts), some of them have come under fire due to their long-term health impact.
It is a good idea for everyone to learn more about these additives, look for them on the labels of the food to be consumed, avoid them as much as possible, and search for information on healthier alternatives. Here’s our comprehensive guide to eating healthy without additives:
Reading the Label
In harmony with the global food standards of Codex Alimentarius Commission and WHO, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has laid down several regulations for the use of preservatives. FSSAI, under the Health Ministry, has fixed the maximum limit for use of additives in various food groups to ensure the acceptable daily intake is not exceeded. It has also stepped up measures to strengthen quality standards while reviewing the existing rules for caffeine content, metal contaminants and other residues in food products.
It is mandatory for a food business operator to declare the preservatives used on the label of a packaged food product. The label, normally found on the back of the package, lists ingredients in the order of their quantity in the food and preservatives (used in small amounts) are most often listed at the bottom.
Additives to Avoid
1. High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS)

Photo Source
Cheap, sweet and produced in abundance as compared to regular sugar, HFCS has crept into food supplies over the past few decades. HFCS can increase your bad cholesterol (LDL) levels, leads to obesity and contribute to the development of diabetes.
2. Aspartame

Photo Source
If you think you’re eating healthy because you’ve replaced your sugar with artificial sweeteners like aspartame, you may want to think again! Problems attributed to these sweeteners include severe headaches, nausea, vertigo, slurred speech, memory loss, blindness, ringing in the ears, loss or change of taste.
3. Monosodium Glutamate (MSG)
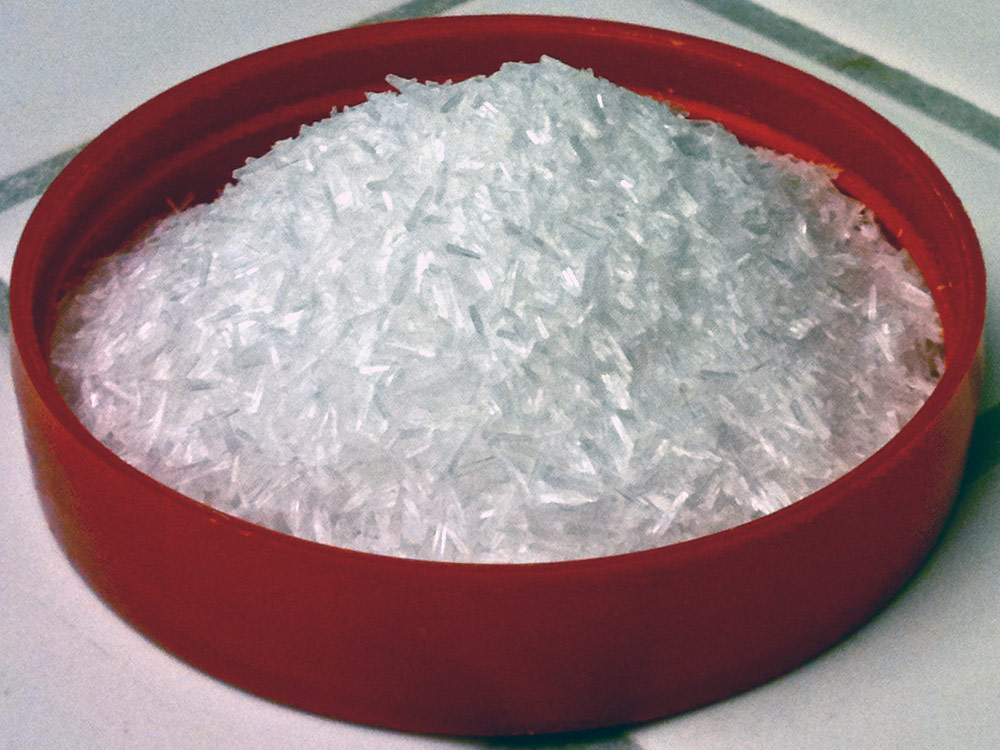

Photo Source
MSG, a salt form of a non-essential amino acid, is a flavour enhancer and common food additive. An excitotoxin, MSG works by triggering the brain to produce excess quantities of the feel-good drug dopamine. Excessive ingestion of MSG can damage cells and result in overeating, which leads to obesity.
4. Potassium Bromate (E924)
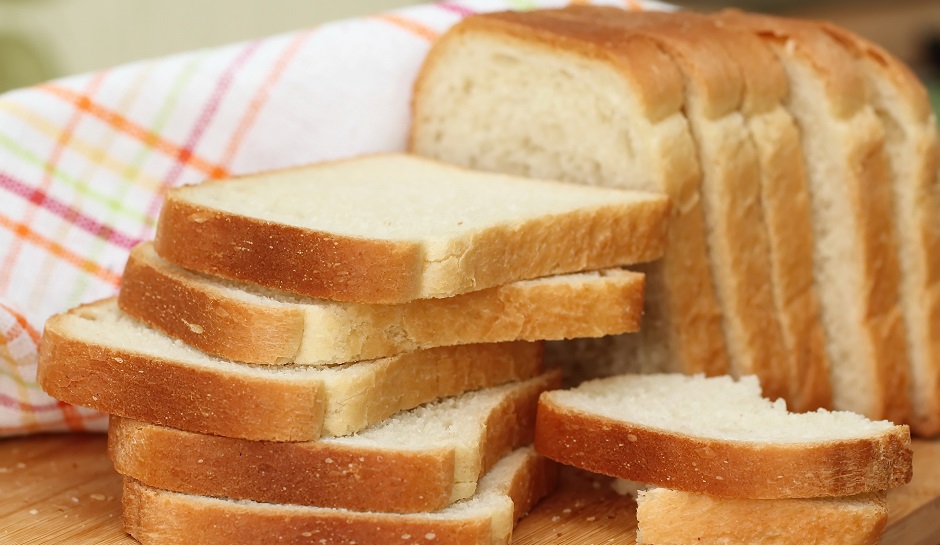

Photo Source
Potassium Bromate is added to bread as a flour enhancer – to make it rise better and give it a uniform consistency. On cooking and heating, it breaks down into bromide, which, when consumed in excess, can inhibit the metabolism of the iodine and is regarded as a possible carcinogenic in countries like Canada, Brazil, Peru, and South Korea. A study by the Centre For Science and Environment (CSE) found that nearly 84 % of commonly available brands of packaged breads in India tested positive for potassium bromate. Following the study, this additive was banned by FSSAI.
5. Diacetyl
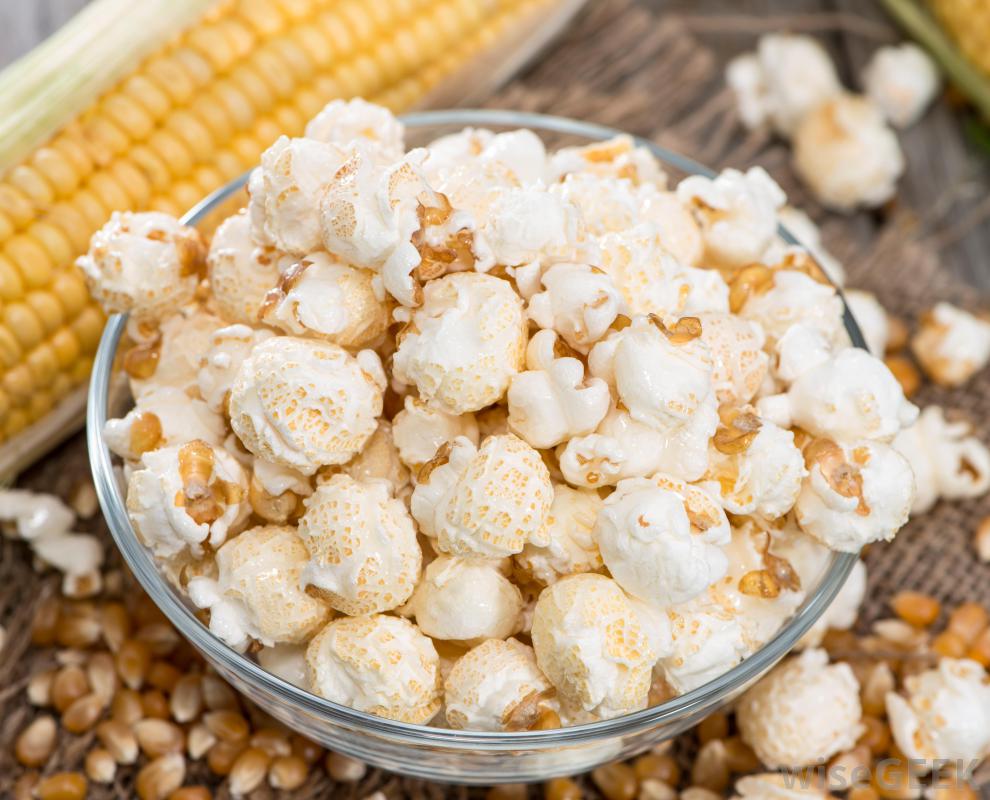

Photo Source
Diacetyl imparts a buttery taste to food. It is a chemical that is naturally present at low concentrations in a wide variety of foods such as dairy, beer, honey and fruits. However, artificially made diacetyl is added to impart the buttery flavour and aroma as well as to delay rancidity in packaged popcorn. The buttery steam of heated diacetyl can directly reach the lungs and excessive amounts can cause lung disease.
6. Sodium Benzoate (E211)

Photo Source
7. Colour Additives

Photo Source
Food dyes are one of the most widely used and dangerous additives. Most of them are petroleum-derived and may contribute to behavioural problems in children like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Some have even been implicated as possible carcinogenics. The use of certain colours in food is permitted but the concentration of these colours has been limited to 100 parts per million. It has also been made mandatory for manufacturers to specify the use of colours on their packages. Now you know why you need to stay way from food and drinks that look unnaturally coloured.
You May Also Like: Now Get Safer, Healthier, Pesticide-Free Food On Your Plate Without Burning A Hole In Your Pocket
Natural Healthier Alternatives
While it’s best to ditch the boxed stuff and go for real foods whenever you can, here are some foods that act as natural preservatives for other foods and are healthy for you too!
Using them in your kitchen can help keep leftovers fresh, keep food items from spoiling quickly and even prevent bacterial growth.
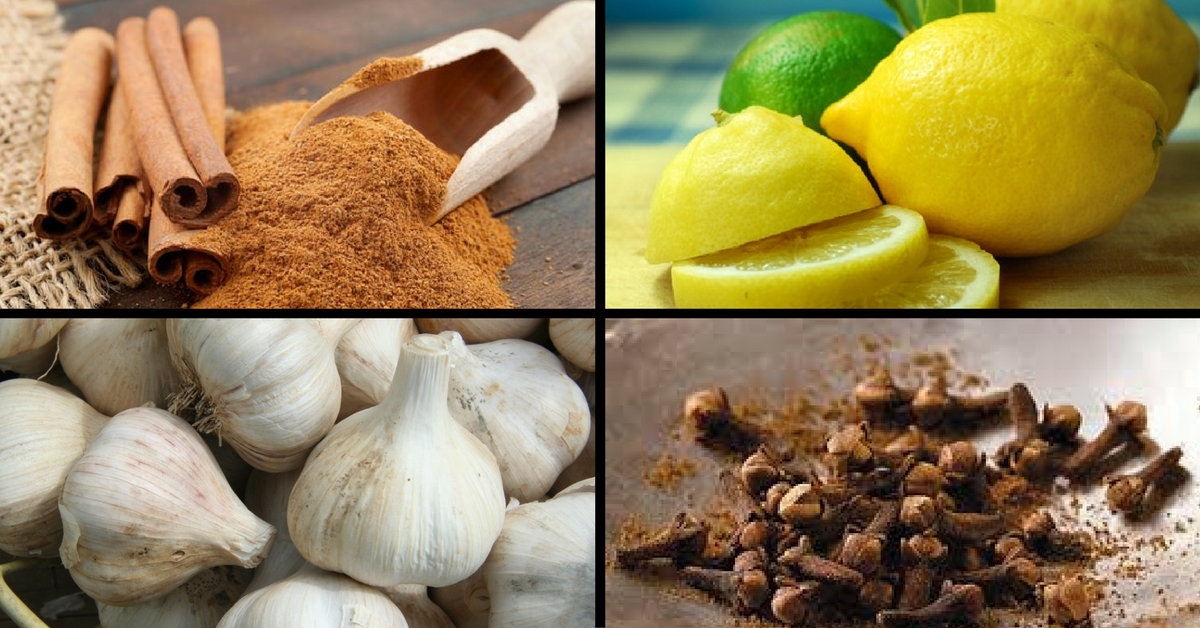

Photo Source : Cinnamon, Lemon, Cloves, Garlic
While you probably use some of them already, there may be others that you haven’t thought of as preservatives.
1. Cloves: Used for thousands of years in India as a natural preservative, cloves contain high amounts of phenolic compounds that have antioxidant properties and also keep food from going bad by preventing the growth of fungus and bacteria.
2. Lemons: Lemons are a natural source of citric acid, an antibacterial preservative found in their peel and flesh. To use them to preserve your food, squeeze them into cold dishes or on top of items right after you cook them.
3. Oregano – Oregano is generally used for its warm herby flavour, but it is a preservative too. It has antioxidant, antibacterial and antifungal properties that can be used to preserve meats.
4. Garlic: Garlic is a potent anti-viral food that’s incredibly good at fighting bacteria — both in your body and in your food. Using garlic in a curry, soup, a dip, or anything else will help ward off harmful bacteria and prevent the food from spoiling quickly.
5. Sage: Sage is used in several cultures as a natural preservative to keep meats and cheeses from going bad. While the herb has antioxidant and antibacterial properties, it needs to be used sparingly to avoid overpowering the food with its strong flavour.
6. Vinegar: Like lemon juice, vinegar is also extremely acidic and is commonly used to preserve pickles and canned foods. The high amounts of acetic acid in vinegar kill microbes and prevent food from going bad.
7. Cinnamon – This aromatic spice has long been used to flavour and preserve food. However, its preservative properties work only against certain microbes and hence, it is best used along with other preservatives.
8. Thyme – Thyme has preservative and antioxidant properties and can be used to prevent food from decaying. However, like cinnamon, it is most effective when it’s used along with other natural preservatives.
Also Read: Fresh Flavours for Your Food: How to Start Your Very Own Herb Garden at Home
Like this story? Have something to share? Email: [email protected], or join us on Facebook and Twitter (@thebetterindia). To get positive news on WhatsApp, just send ‘Start’ to 090 2900 3600 via WhatsApp.
This story made me
- 97
- 121
- 89
- 167
Tell Us More
We bring stories straight from the heart of India, to inspire millions and create a wave of impact. Our positive movement is growing bigger everyday, and we would love for you to join it.
Please contribute whatever you can, every little penny helps our team in bringing you more stories that support dreams and spread hope.